The story of Indian companies going global represents one of the most remarkable transformations in international business. What started as modest ventures in the 1960s has evolved into a powerful wave of global expansion, with Indian companies now competing successfully in markets worldwide.
The Three Waves of Indian Global Expansion
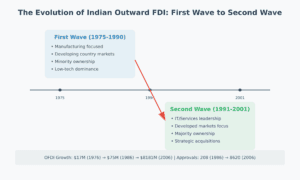
The First Wave (1960s-1991) Picture a time when Indian businesses took their first tentative steps abroad:
- Small joint ventures in developing countries
- Basic manufacturing and trading
- Strictly regulated overseas investments
- Focus on neighboring Asian and African markets
The Transition Phase (1991-2000) The winds of change arrived with economic liberalization:
- Relaxed regulations on overseas investment
- Growing technological capabilities
- Software companies leading the charge
- First major international acquisitions
The Global Surge (2000-Present) Indian companies transformed into confident global players:
- Major international acquisitions
- Technology and knowledge-seeking investments
- Diverse industry presence from IT to pharmaceuticals
- Competition with established global players

What Makes Indian Multinationals Different?
Unlike traditional Western multinationals or even their Chinese counterparts, Indian companies show some unique characteristics:
- Strong private sector leadership
- Focus on knowledge-intensive industries
- Innovative adaptation of technologies
- Balanced mix of partnerships and acquisitions
The Power of the Indian Conglomerate
One distinctive feature is the role of Indian business groups or conglomerates. These organizations have unique advantages:
- Ability to share resources across businesses
- Strong financial capabilities
- Deep management expertise
- Diverse industry experience
Looking Ahead
As Indian companies continue their global journey, they face both opportunities and challenges:
Opportunities:
- Access to new markets and technologies
- Strategic partnerships
- Resource security
- Global talent pools
Challenges:
- Cross-cultural integration
- Technology gaps
- International competition
- Resource mobilization
The rise of Indian multinationals represents more than just business expansion – it signals the emergence of a new model of global enterprise that combines technological capability with cost innovation, global ambition with local understanding.
This transformation continues to reshape not only Indian business but also the global economic landscape, creating new possibilities for international cooperation and development. As these companies evolve, they are not just adapting to global standards but are increasingly setting new ones, particularly in areas like IT services, pharmaceuticals, and automotive components.
The story of Indian companies’ global expansion demonstrates that emerging market firms can successfully compete on the world stage while maintaining their unique characteristics and advantages. Their journey offers valuable lessons for understanding the changing nature of global business in the 21st century.
Academic Abstract:
This volume examines the rise of Indian multinational enterprises (MNEs) and their growing significance in global business through a collection of empirical studies and analytical frameworks. Drawing on extensive firm-level data and case studies across industries, the volume analyzes the evolution, drivers, and patterns of Indian outward foreign direct investment (OFDI) since the 1960s, with particular focus on the acceleration post-2000. The studies reveal that Indian MNEs have moved beyond their traditional focus on South-South investment to emerge as significant players in developed markets, driven by both market-seeking and strategic asset-seeking motivations. The volume highlights the distinctive characteristics of Indian MNEs, including their strong presence in knowledge-intensive sectors, the role of business conglomerates, and their balanced use of partnerships and acquisitions for international expansion. Through detailed analyses of pharmaceutical, software, automotive and other industries, the research demonstrates how Indian firms have leveraged their technological capabilities, cost advantages, and innovative adaptation skills to compete globally. The volume also explores the policy environment, institutional frameworks, and challenges faced by Indian MNEs in their internationalization journey. This collection makes an important contribution to understanding the changing dynamics of emerging market multinationals and offers insights for theory, policy, and practice in international business.
Learn More:
Full citation: K. P. Sauvant and Jaya Prakash Pradhan with K. P. Sauvant, A. Chatterjee and B. Harley (eds.) (2010), The Rise of Indian Multinationals: Perspectives on Indian Outward Foreign Direct Investment, New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
Learn More: